Europium Oxide
- About
- Specification
- References
- Price information
- Video
- tab 6
- tab 7
- tab 8
- tab 9
- tab 10
- tab 11
- tab 12
- tab 13
- tab 14
- tab 15
- tab 16
- tab 17
- tab 18
- tab 19
- tab 20
Europium is most commonly extracted from monazite and bastnasite ores.
Europium is the most reactive of the rare earth elements. It rapidly oxidizes in air: bulk oxidation of a centimeter-sized sample occurs within several days. It resembles calcium in its reaction with water.
Europium oxide is widely used as a red or blue phosphor in television sets and fluorescent lamps, as an activator for yttrium-based phosphors, for manufacturing fluorescent glass and as anti-counterfeiting phosphor in banknotes.
Europium is the most reactive of the rare earth elements. It rapidly oxidizes in air: bulk oxidation of a centimeter-sized sample occurs within several days. It resembles calcium in its reaction with water.
Europium oxide is widely used as a red or blue phosphor in television sets and fluorescent lamps, as an activator for yttrium-based phosphors, for manufacturing fluorescent glass and as anti-counterfeiting phosphor in banknotes.
Appearance: White solid
Purity: Eu2O3/TREO ≧99.99% as per China industrial standard GB/T 3504-2015
Test methods: GB/T 14635 and GB/T 18115.9
Purity: Eu2O3/TREO ≧99.99% as per China industrial standard GB/T 3504-2015
Test methods: GB/T 14635 and GB/T 18115.9
Chemical formula: Eu2O3
CAS No.: 1308-96-9
EINECS EC No.: 215-165-6
HS-Code: 2846901400
Industrial standard: GB/T 3504-2015
CAS No.: 1308-96-9
EINECS EC No.: 215-165-6
HS-Code: 2846901400
Industrial standard: GB/T 3504-2015
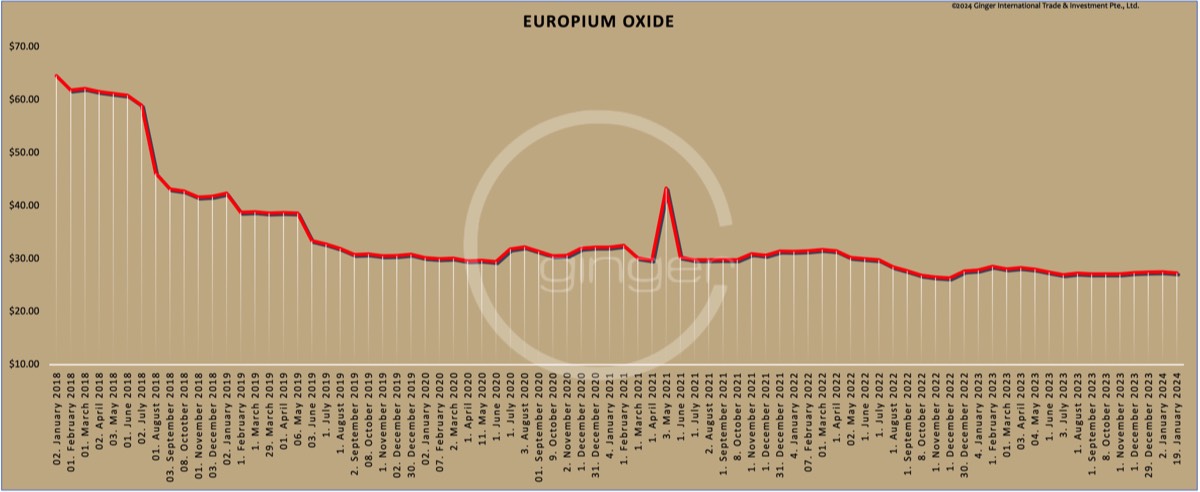
Price level of europium oxide on [prices-B1] was ca. [prices-B11]/kg net Ex Works China, incl. 13% VAT.
This is not an offer, it is a general price information. Please use at your own risk.
If you need a specific offer, please contact us and we will be delighted to serve you.

